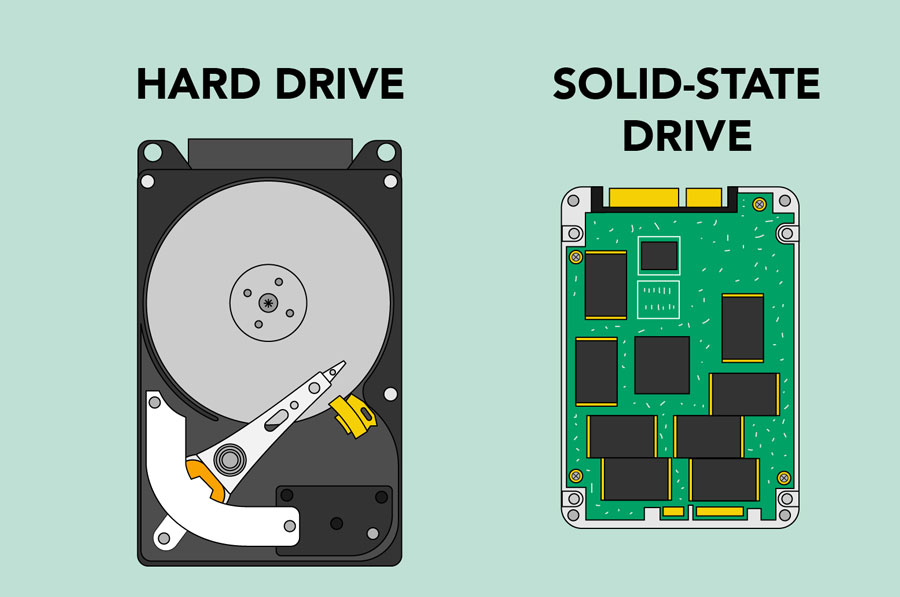
1. The hard drive is a storage device responsible for storing permanent and temporary data. This data comes in many different forms, but is essentially anything saved or installed to a computer: for example, computer programs, family photos, operating system, word-processing documents, and so on.
2. A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk[b] is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage and one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces.[2] Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data even when powered off.[3][4][5] Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box.
3. Introduced by IBM in 1956,[6] HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely on flash memory storage devices. More than 224 companies have produced HDDs historically, though after extensive industry consolidation most units are manufactured by Seagate, Toshiba, and Western Digital. HDDs dominate the volume of storage produced (exabytes per year) for servers. Though production is growing slowly (by exabytes shipped[7]), sales revenues and unit shipments are declining because solid-state drives (SSDs) have higher data-transfer rates, higher areal storage density, somewhat better reliability,[8][9] and much lower latency and access times.
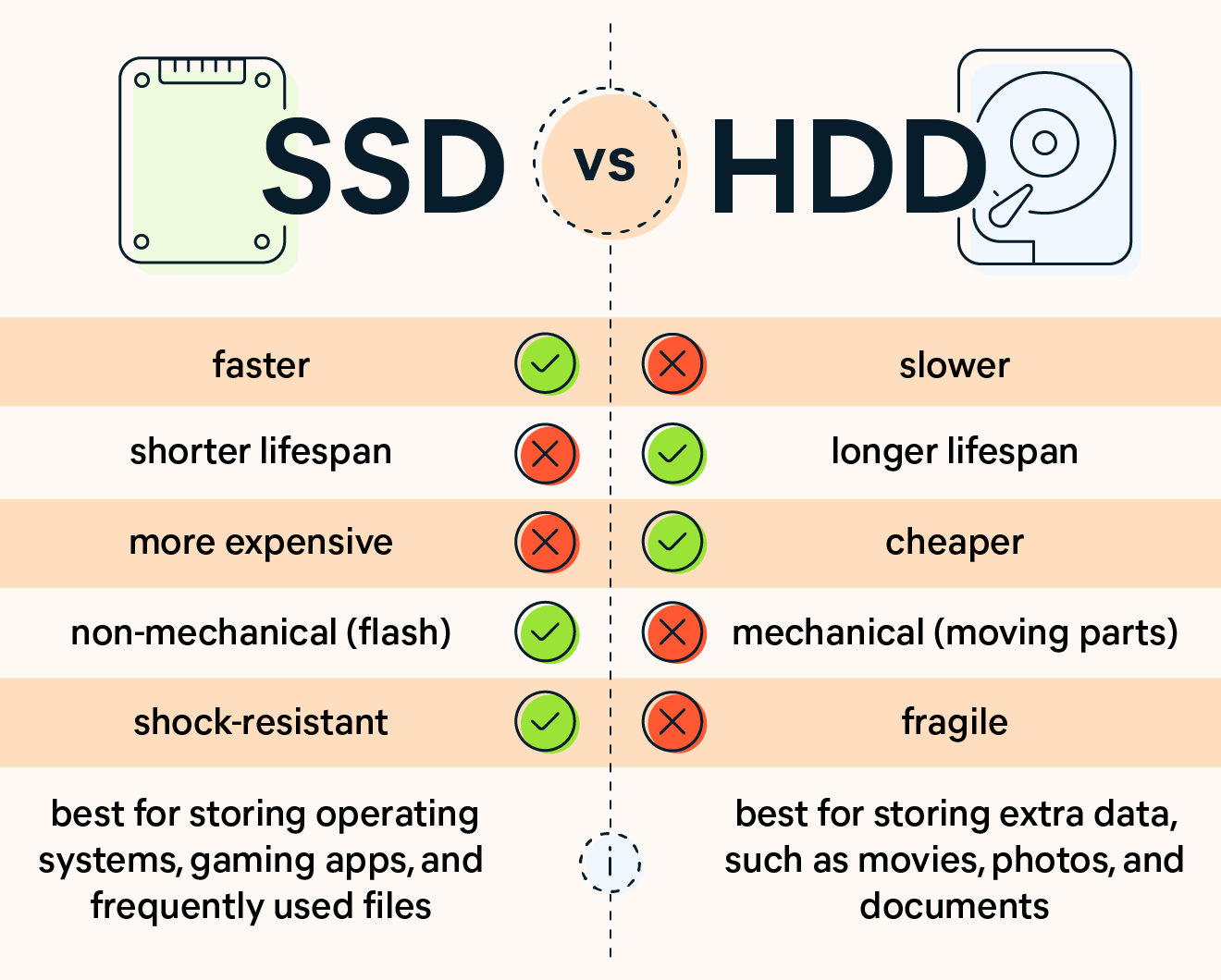
4. The speed difference between solid state drives vs hard disk drives is significant. SSDs are extremely fast in all areas, but the speed difference is more pronounced when performing certain tasks, such as: Sequential read/write operations: The speed difference of an SSD vs hard drive is most apparent when copying and moving huge files. HDDs can copy 30 to 150 MB per second (MB/s), while standard SSDs perform the same action at speeds of 500 MB/s. Newer NVME SSDs can even show speeds of up to an astounding 3,000 to 3,500 MB/s. With an SSD, you can copy a 20 GB movie in less than 10 seconds, while a hard disk would take at least two minutes. Upgrading your Mac to an SSD or installing an SSD in your PC will give it a significant speed boost. Small 4K read/write operations: Most of the time, when you run your OS, open basic programs, or browse the web, you’re actually opening and manipulating thousands of smaller files, which are stored in small blocks of data (usually sized at 4K). The faster your disk can read and write these 4K blocks, the faster and snappier your system operates. With HDDs, the speed ranges from 0.1 to 1.7 MB/s. SSDs and NVME SSDs operate at much faster speeds of 50 to 250 MB/s.